
Cooperative Urban
Mobility Portal
Explore Connected and Cooperative Mobility

Cooperative
Urban Mobility Portal
Explore Connected and Cooperative Mobility
Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC)
The service ensures smooth driving of vehicles with enabled Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC) function or platooning for driving through a (series of) C-ITS equipped intersection(s).
Participating actors in Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control include city’s authorities which would like to prepare their infrastructure to the arrival of autonomous vehicles and companies selling intelligent traffic light solutions.
The objective of Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control is to improve safety, comfort and traffic flow on intersections with Vehicle-to-Infrastructure communication between CACC and intersection traffic lights (or managed intersections).
Invisible
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Business models
TTaking into account various stakeholders’ views, a list of business model blueprints that address current or future challenges of urban areas, together with their operating and value-capture scenarios depicting the inner-workings of the business models, and the exchange of costs-benefits among stakeholders, have been created for the Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control service.
Invisible
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Architecture
ITS-G5
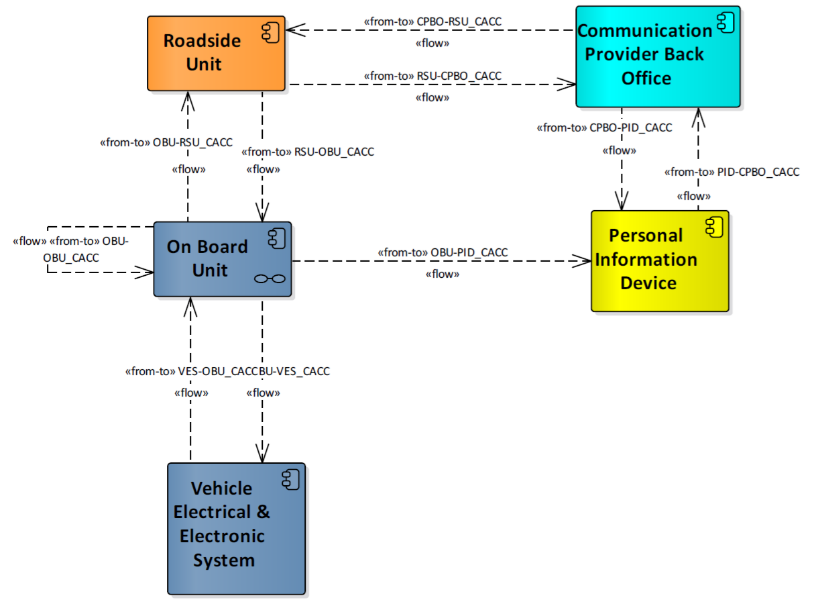
In case of ITS-G5 communication technologies the On-Board Unit broadcasts its information needed for vehicle following and/ or platooning state information. This use case is based on Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication only in which the ego vehicle application uses the information from the Vehicle Electrical & Electronic System (VEES) to construct the messages to be broadcasted out of the On-Board Unit. The application status is based on information from VEES and presented on the vehicle Human Machine Interface. In the use where passenger vehicles approach urban environment, vehicle speeds are relatively slow and the use case is extended with information from traffic light controllers at cooperative intersections. This is based on Infrastructure-to-Vehicle communication with a Roadside Unit. The On-Board Unit uses the Traffic Light Controller data and this can be used to adapt CACC set points at the VEES. In the use case of Truck Platooning the focus is also on deployment in (semi-)urban environments were interaction with cooperative intersections helps the truck platoon passing these urban environments. So in addition to previous use cases, the focus is on “priority services” for the truck platoon in which the truck On-Board Unit uses a priority request.
Cellular
In case of cellular communication technologies in the use case where passenger vehicles approach urban environment, the vehicle speeds are relatively slow and the use case is extended with information from traffic light controllers at cooperative intersections. This information is provided via connected services Communication Provider Back Office. The Traffic Light Controller data from Roadside Unit is provided via to a central Communication Provider Back Office. The Traffic Light Controller data is provided to the vehicle Personal Information Device. Physical in-vehicle implementations can have separate components integrated. As example a Personal Information Device can be a smart phone or be part of a hybrid On-Board Unit, also a Personal Information Device can be part of existing vehicle Human Machine Interface.
Invisible
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Architecture schema
Detailed information about Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control architecture can be found here.
Invisible
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Within the C-MobILE project the Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control service is implemented in four Deployment Sites: Bordeaux, Newcastle, North Brabant, and Vigo.
Invisible
Bordeaux
In Bordeaux the CACC service is implemented as a proof of concept in a limited part of A63 highway. The services is based on ITS-G5 communication technology to enable trucks to exchange CAM messages and use CAN bus communication. By exchanging data via their OBU truck can adapt their respective speed and drive in platoon. The service provider for CACC is NeoGLS.
Invisible
Newcastle
Invisible
North Brabant
Invisible
Vigo



This website has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme
under Grant Agreement number 723311.
