Blind Spot Detection (BSD)
The objective of Blind Spot Detection warning is to provide timely in-car driving assistance information on the presence of a vehicle in a designated blind spot location in the driving direction of the vehicle.
Taking into account various stakeholders’ views, a list of business model blueprints that address current or future challenges of urban areas, together with their operating and value-capture scenarios depicting the inner-workings of the business models, and the exchange of costs-benefits among stakeholders, have been created for the Blind Spot Detection warning service.
Detailed information about Blind Spot Detection architecture can be found here.
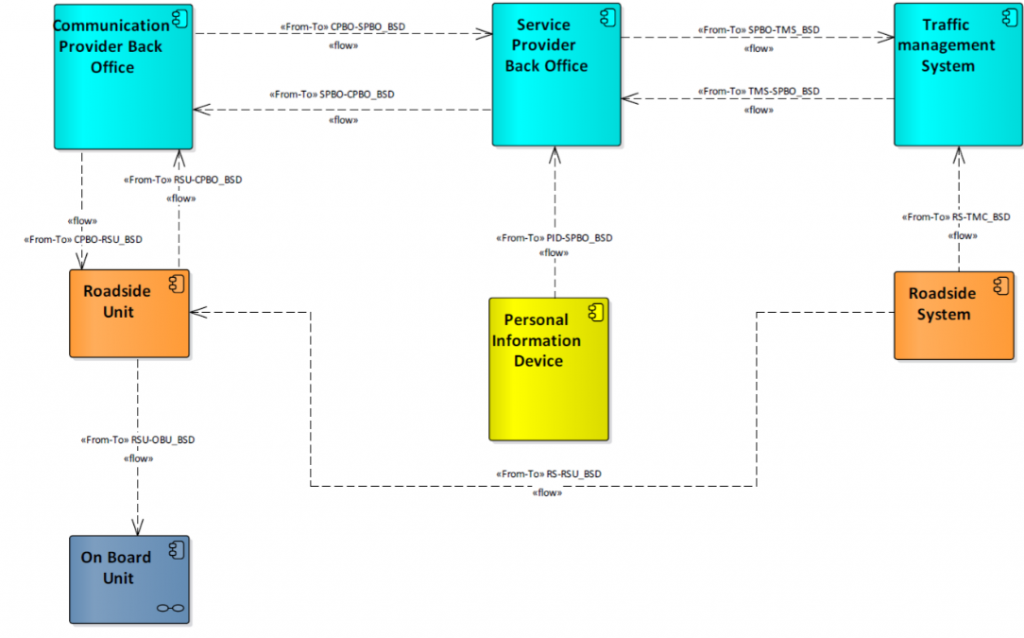
Within the C-MobILE project the Blind Spot Detection service is implemented in four Deployment Sites: Bilbao, Bordeaux, and North Brabant.
In Bilbao the Blind Spot Detection service is implemented using cellular communication technology. The service warns vulnerable road users (and specifically cyclists) about the risk of collision with other vehicles when they are approaching a blind spot in the city road network. CEIT is the service and App provider ensuring timely alerts to VRUs.
Note: This service is currently deployed as a proof of concept.
In Bordeaux the Blind Spot Detection service is implemented using both cellular and ITS-G5 communication technologies. This service uses vehicle to vehicle communication to trigger alerts when a vulnerable road user (i.e. motorcyclist or cyclist) is detected and potentially out of sight for the vehicle driver. The service provider of BSD is NeoGLS and the service is available through the App “CTD – Connected Mobility”.
In North Brabant the Blind Spot Detection service is implemented (as a proof of concept) using cellular communication technology. The service warns vulnerable road users (and specifically cyclists) about the risk of collision with other vehicles when they are approaching a blind spot in the city road network. This service is ensured thanks to the camera detection system developed and deployed by Macq.