Safety C-ITS Services
- Road Works Warning (RWW)
- Road Hazard Warning (RHW)
- Emergency Vehicle Warning (EVW)
- Signal Violation Warning (SVW)
- Warning System for Pedestrian (WSP)
- Emergency Brake Light (EBL)
- Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC)
- Slow or Stationary Vehicle Warning (SSVW)
- Motorcycle Approaching Indication (MAI)
- Blind Spot Detection (BSD)
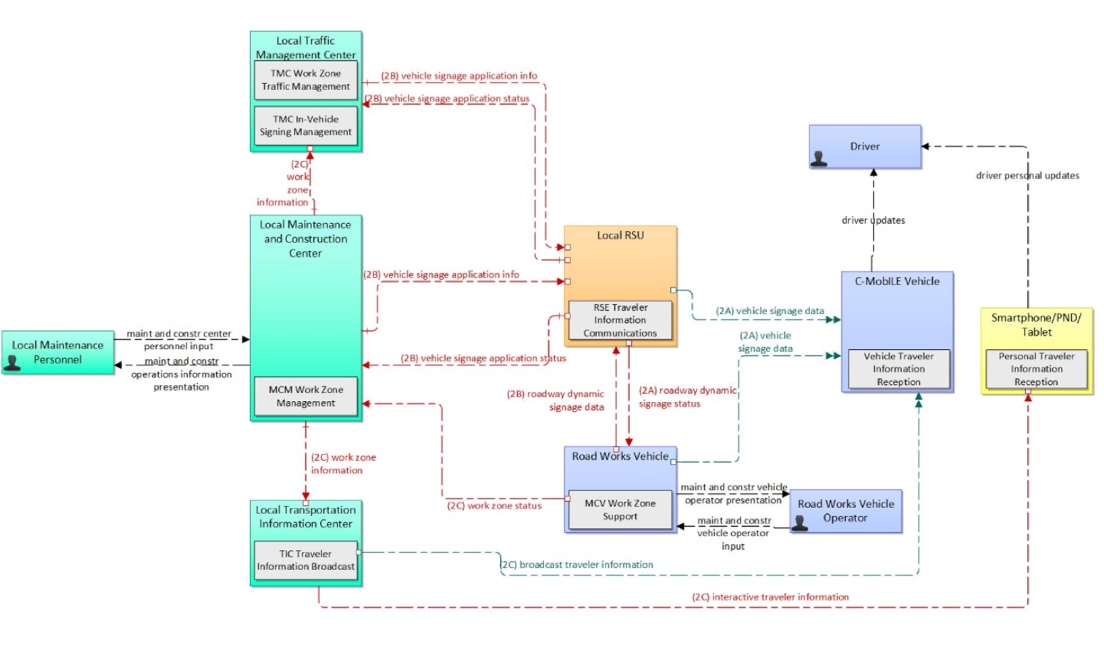
For Road Works Warning (RWW) service operation road works data from different sources should be collected and a database for storing roadworks data shall be available. Such information should be managed and handled by a server, for example in a Traffic Management System, in case of cellular communication technologies. The service shall be able to determine if a vehicle is inside the relevance area of a roadworks situation, which depends on the type of roadwork and road, while messages’ maximum delay should be 100ms.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package Work Zone Management, with customizations to support local user needs.

Road Hazard Warning (RHW) aims to inform the drivers in a timely manner of upcoming, and possibly dangerous events and locations. This allows drivers to be better prepared for the upcoming hazards and make necessary adjustments and manoeuvres in advance.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package Queue Warning, with customizations to support local user needs.

Emergency Vehicle Warning (EVW) uses information provided by the emergency vehicle to inform a driver of another vehicle about an approaching emergency vehicle even when the siren and light bar of the emergency vehicle may not yet be audible or visible. This is also known as “Emergency Vehicle Alert (EVA)”, which alerts the driver about the location and the movement of public safety vehicles responding to an incident so the driver does not interfere with the emergency response. The service is enabled by receiving information about the location and status of nearby emergency vehicles responding to an incident.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package V2V Special Vehicle Alert, with customizations to support local user needs.
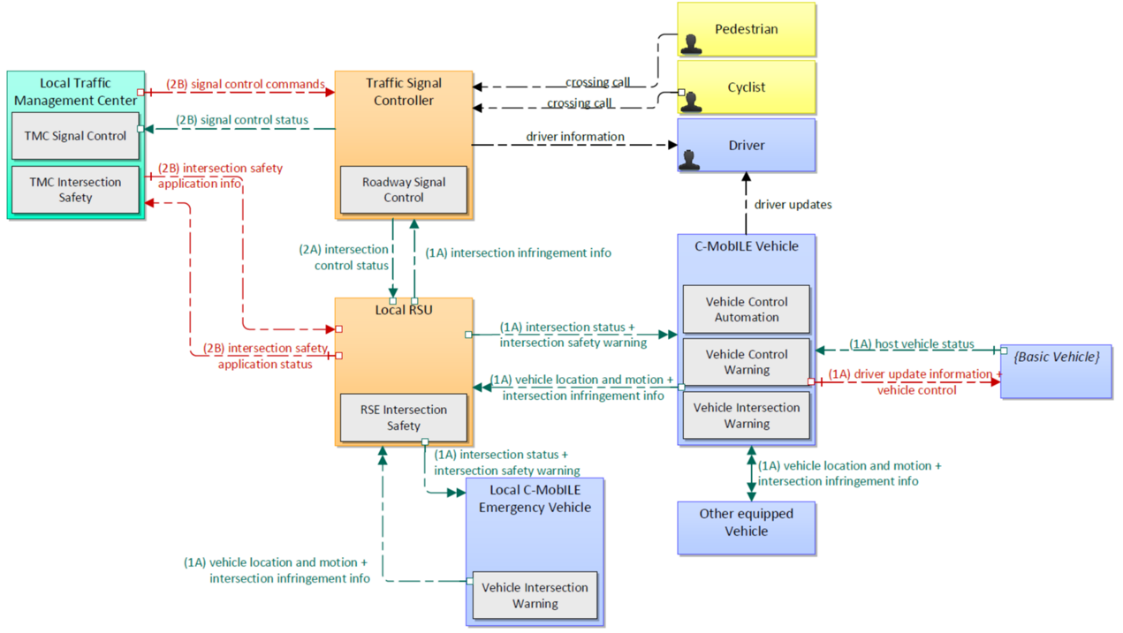
Signal Violation Warning (SVW) aims to reduce the number and severity of collisions at signalised intersections by warning drivers who are likely -due to high speed- to violate a red light. Also known as the “Signal violation/Intersection Safety” or “Red Light Violation Warning”.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package Intersection Safety Warning and Collision Avoidance, with customizations to support local user needs.
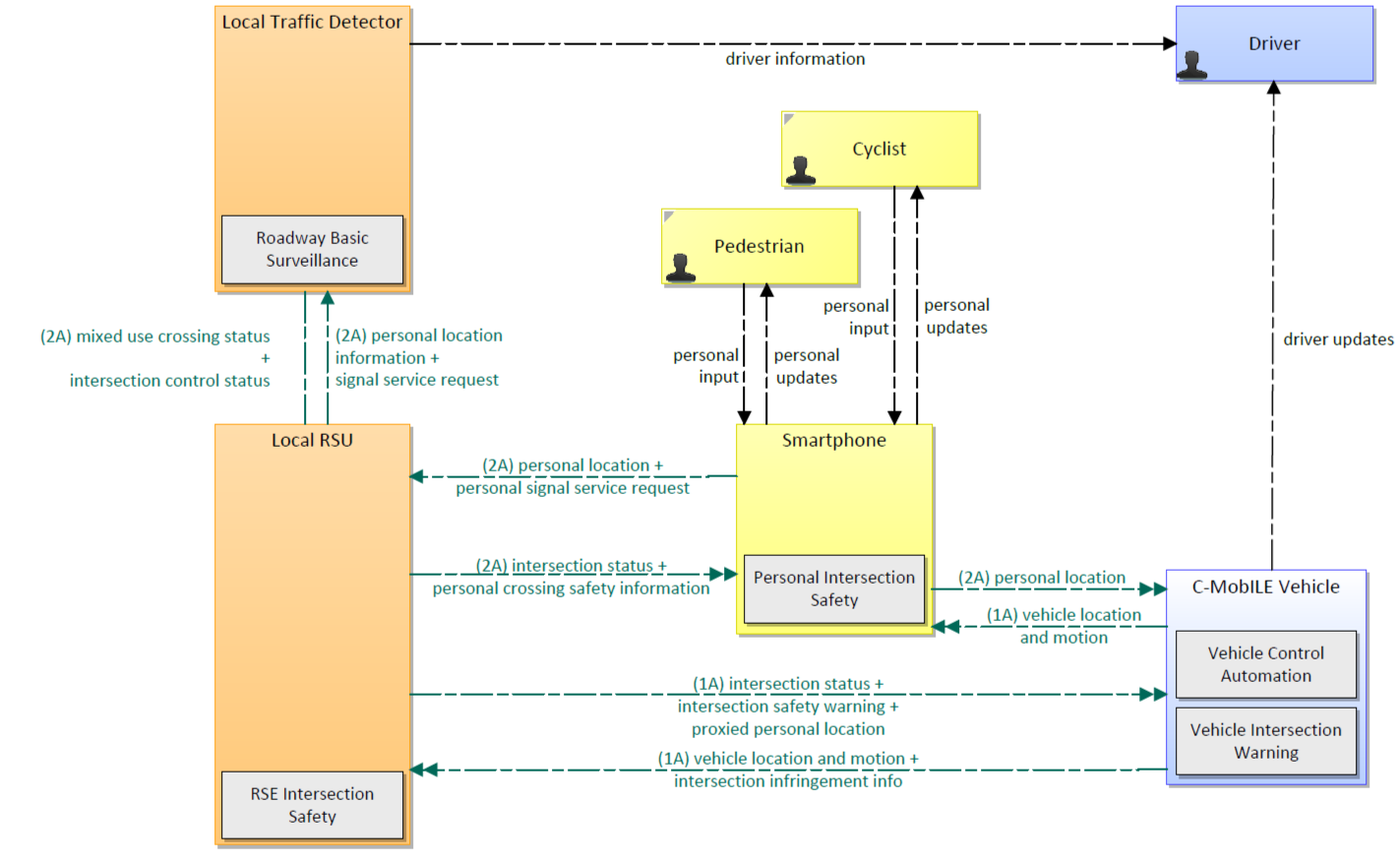
Warning System for Pedestrian (WSP) aims to detect risky situations (e.g. road crossing) involving pedestrians, allowing the possibility to warn vehicle drivers. Hence, the warning is based on pedestrian detection. The scope of the service can be extended to cover other Vulnerable Road Users (e.g. cyclists). The service is particularly valuable when the driver is distracted or visibility is poor. The service is also known as “Vulnerable road user Warning”.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety, with customizations to support local user needs.
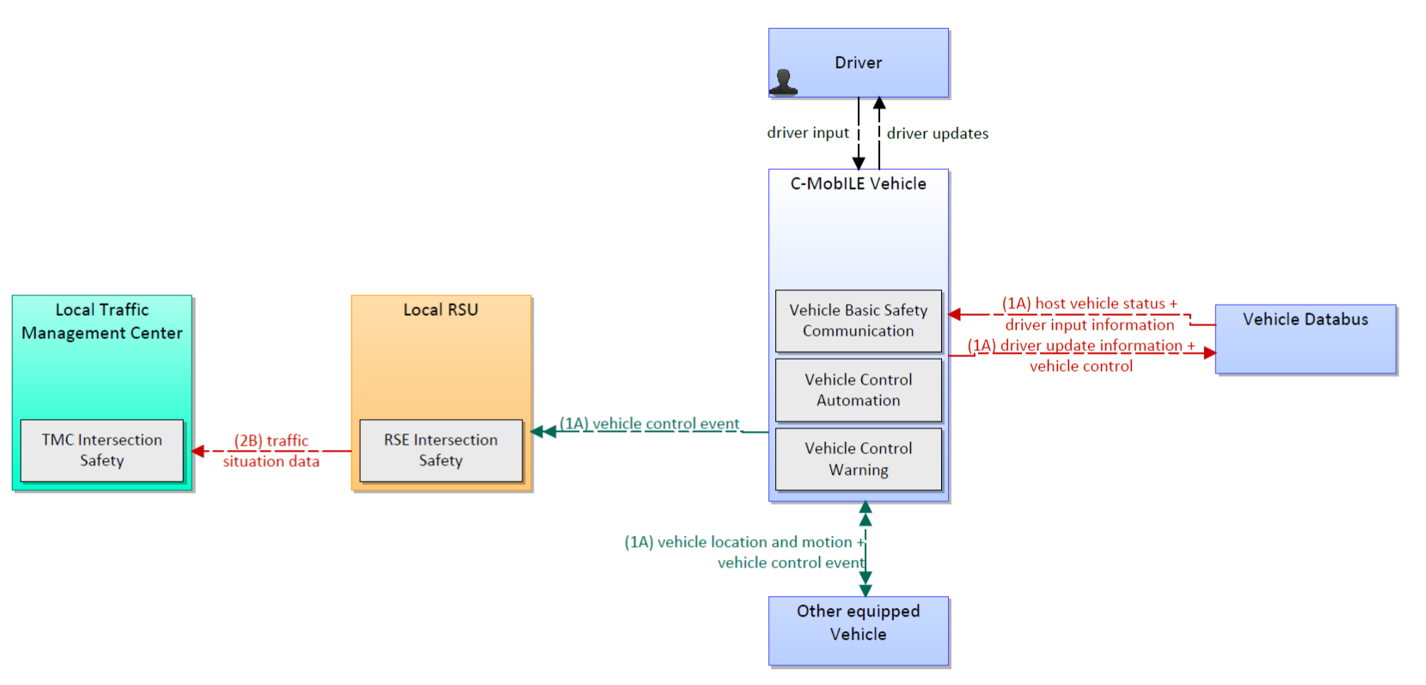
Emergency Brake Light (EBL) aims to avoid (fatal) rear end collisions, which can occur if a vehicle ahead suddenly brakes, especially in dense driving situations or in situations with decreased visibility. The driver is warned before s/he is able to realize that the vehicle ahead is braking hard, especially if s/he does not see the vehicle directly (vehicles in between).
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package V2V Basic Safety, with customizations to support local user needs.
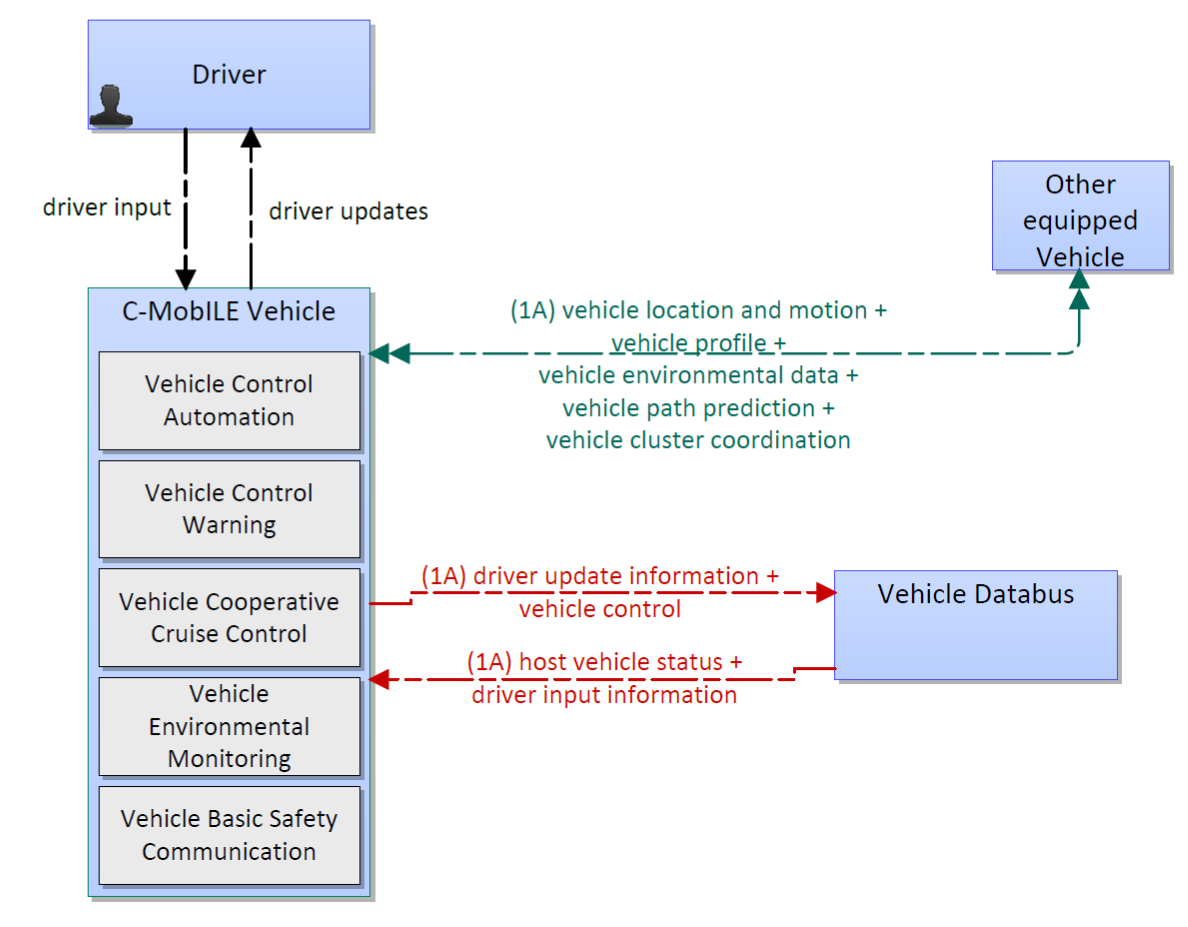
Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC) represents an evolutionary advancement of conventional cruise control (CCC) and adaptive cruise control (ACC) by utilizing V2V communications to automatically synchronize the motion of many vehicles. While ACC uses Radar or LIDAR measurements to derive the range to the vehicle in front, CACC also takes the preceding vehicle’s acceleration into account.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control, with customizations to support local user needs.
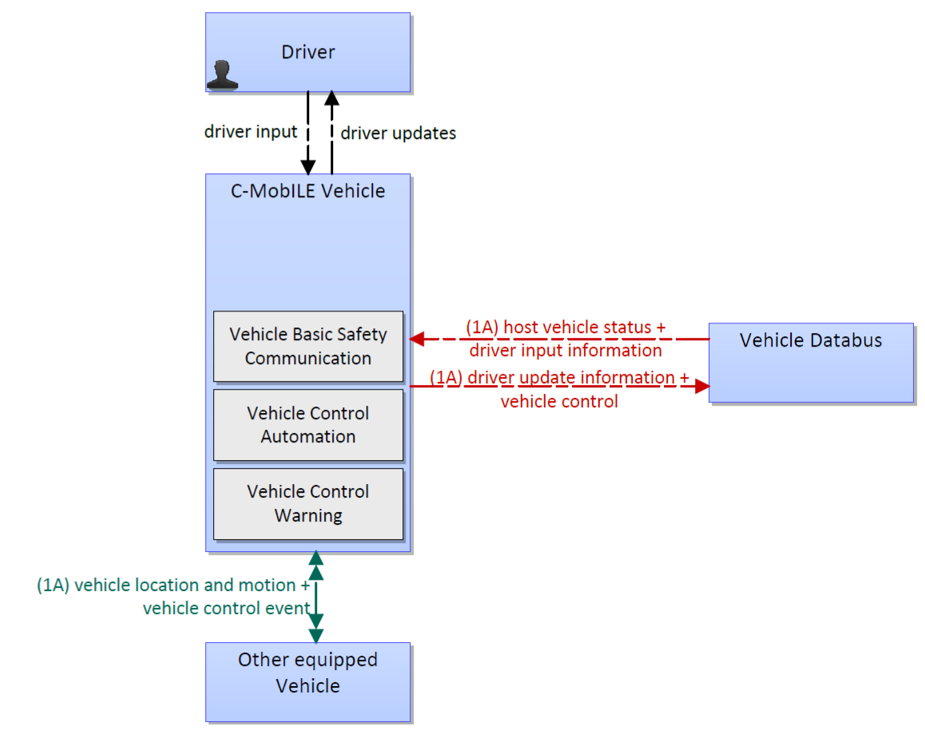
Slow or Stationary Vehicle Warning (SSVW) aims to inform/ alert approaching vehicles of (dangerously) immobilized, stationary or slow vehicles that impose significant risk.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package V2V Basic Safety, with customizations to support local user needs.
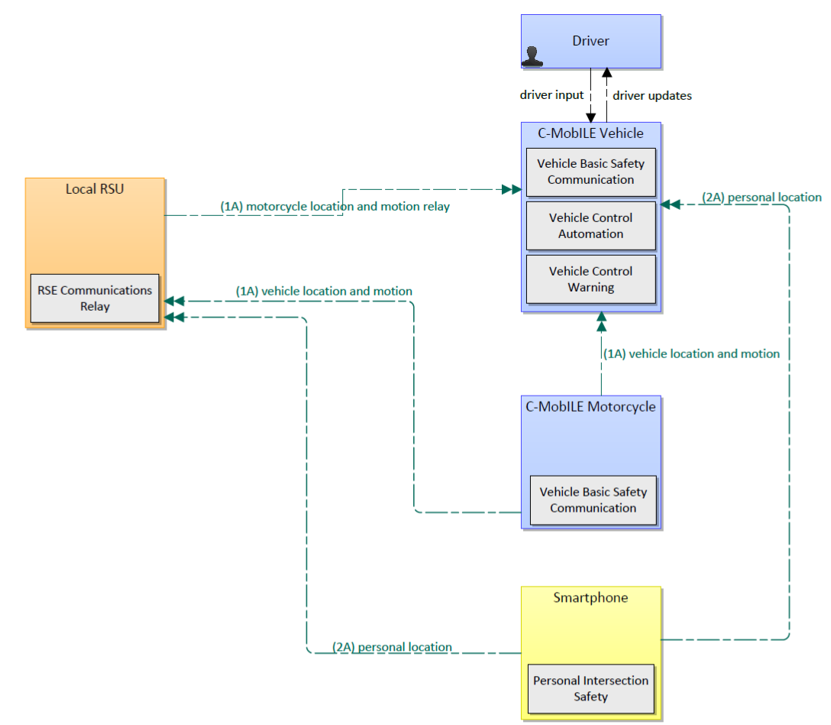
Motorcycle Approaching Indication (MAI) informs the driver of a vehicle that a motorcycle is approaching/passing. The scope can be extended to cover other VRUs, such as cyclists and other Powered Two Wheelers (PTW). The motorcycle could be approaching from behind or crossing at an intersection.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package V2V Basic Safety, with customizations to support local user needs.

Blind Spot Detection (BSD) aims to detect and warn the drivers about other vehicles of any type located out of sight.
This service architecture is largely based on the ARC-IT service package V2V Basic Safety, with customizations to support local user needs.