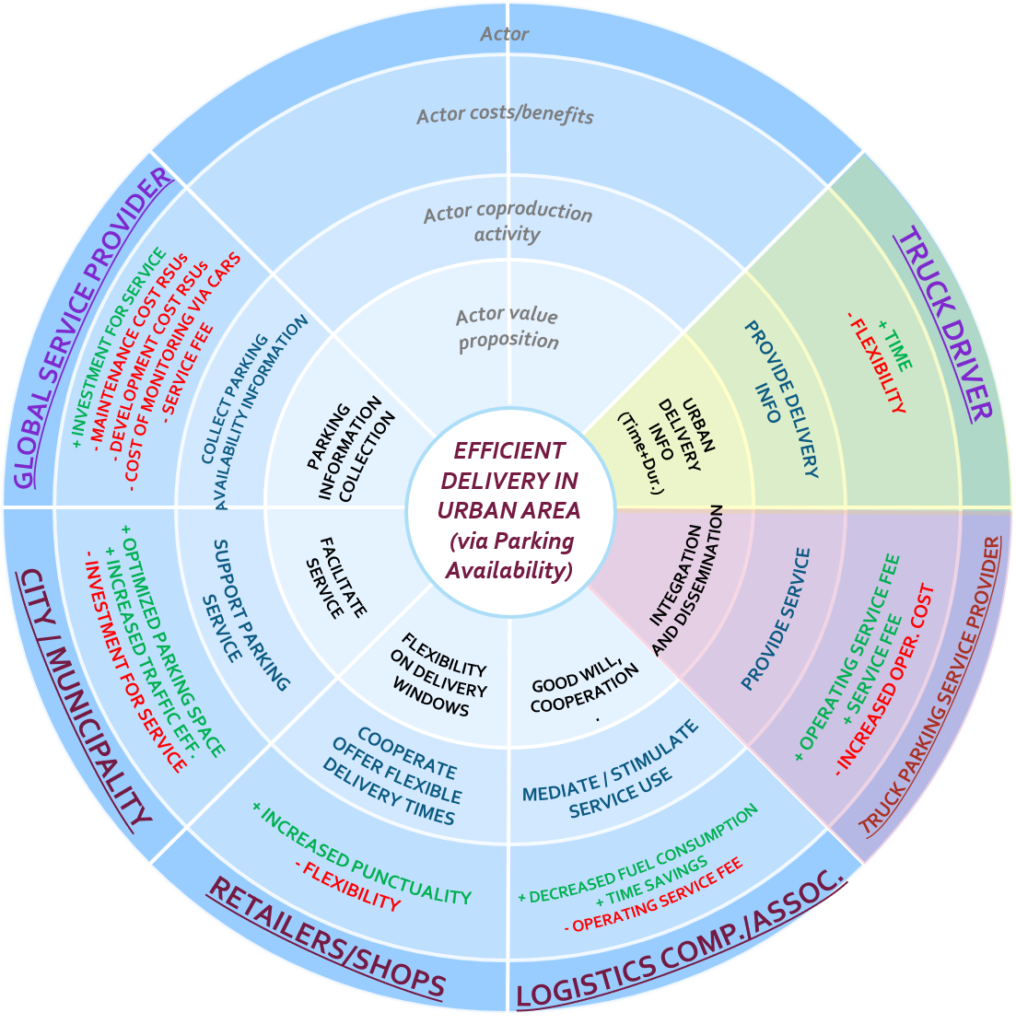
Business scenario
Freight transport is essential in urban areas for replenishing stocks of various merchandise in shops and markets and delivering parcels and other supplies to offices in center locations. However, despite the critical need, the freight delivery in urban areas has several adverse effects, such as increased traffic congestion and disruption, and increased air and noise pollution. These effects are amplified in city centers for which providing sufficient loading and unloading spots are problematic, yet not managed effectively. The business model blueprinted above targets at the issues regarding traffic disruption due to urban freight transportation. It does so by bringing structure into the management of parking process and capacity during urban freight delivery using the parking availability service.
Business model blueprint
The objective of the business model is to offer efficient freight delivery in the urban areas with the aim to decrease related traffic disruptions and incidents. The business model blueprint is enabled by an application for which a dedicated truck parking service provider offers time and availability information about parking spots that are allocated for freight delivery, and truck drivers of logistics companies or of specific associations indicate their urban delivery information through reservation. Such parking management schemes are necessary to bring a structure into the related process. However, these schemes are effective only when all relevant stakeholders collaborate closely and the system is operated and monitored effectively.
The key stakeholders for the business model design include the city / municipality, a global service provider, a truck parking provider and the logistics companies (as representatives of the truck drivers). The city owns the private and public parking spaces is in the city and should indicate what parking spaces are suitable for truck parking. In addition, the city is responsible for facilitating the service deployment and operation, investing in the service operations conducted by the global service provider. This global service provider is tasked with generating the parking information, such that this information can be communicated to a dedicated truck parking service provider. The truck parking service provider consequently enables the service for logistics companies, such that its truck drivers can efficiently and effectively find and reserve a suitable parking location given their indicated time slots and availability. As a result, although the truck drivers can be less flexible in the time-window for their delivery, they spend less time (and fuel) for looking for appropriate parking spots and benefit from securing a parking spot that can be more appropriate for loading/unloading. Trucks that stay longer than their reserved time-slot can be subject to increased parking rates or fines. To stimulate truck drivers to use and adhere to the information provided through the service, logistics companies are included as an explicit actor to do so. Accordingly, logistics companies are responsible for ensuring that truck drivers comply to the parking advice provided through the service solution. In exchange for service use, the logistics companies pay a service fee to the truck parking service provider.
To further support the business model design, retailers in the city can be included as stakeholders, contributing to the business model design through offering flexibility to truck drivers with respect to the delivery windows. Through increasing the delivery windows or providing flexibility with regards to when deliveries can be made, an increased amount of time slots per parking space can become available for truck drivers, which in turn may motivate truck drivers to comply to the parking advice given through the service.
Business model viability
Use of the service solution by truck drivers has significant positive effects on the time required to find a suitable parking spot and the decrease in fuel consumption as a result of this. Accordingly, stimulated use of the service can yield considerable monetary benefits for the logistics companies (in terms of time savings, fuel consumption) which can offset the service fees incurred for use of the service. Whilst the city is expected to incur fixed upfront investment costs to support service deployment and maintenance, the benefits generated in terms of traffic optimization, decreased pollution and a decreased need for parking space should offset these costs in the long term.